TimeStretch
Added in v0.2.0
Change the speed or duration of the signal without changing the pitch. This transform lets you choose
between method="signalsmith_stretch" and method="librosa_phase_vocoder". If you need other time stretching methods,
consider the following alternatives:
- atempo in ffmpeg
- Rubber Band library
- https://github.com/KAIST-MACLab/PyTSMod
- https://github.com/vinusankars/ESOLA
Input-output example
In this example we speed up a sound by 25% (i.e. a rate of 1.25), using the signalsmith_stretch method:
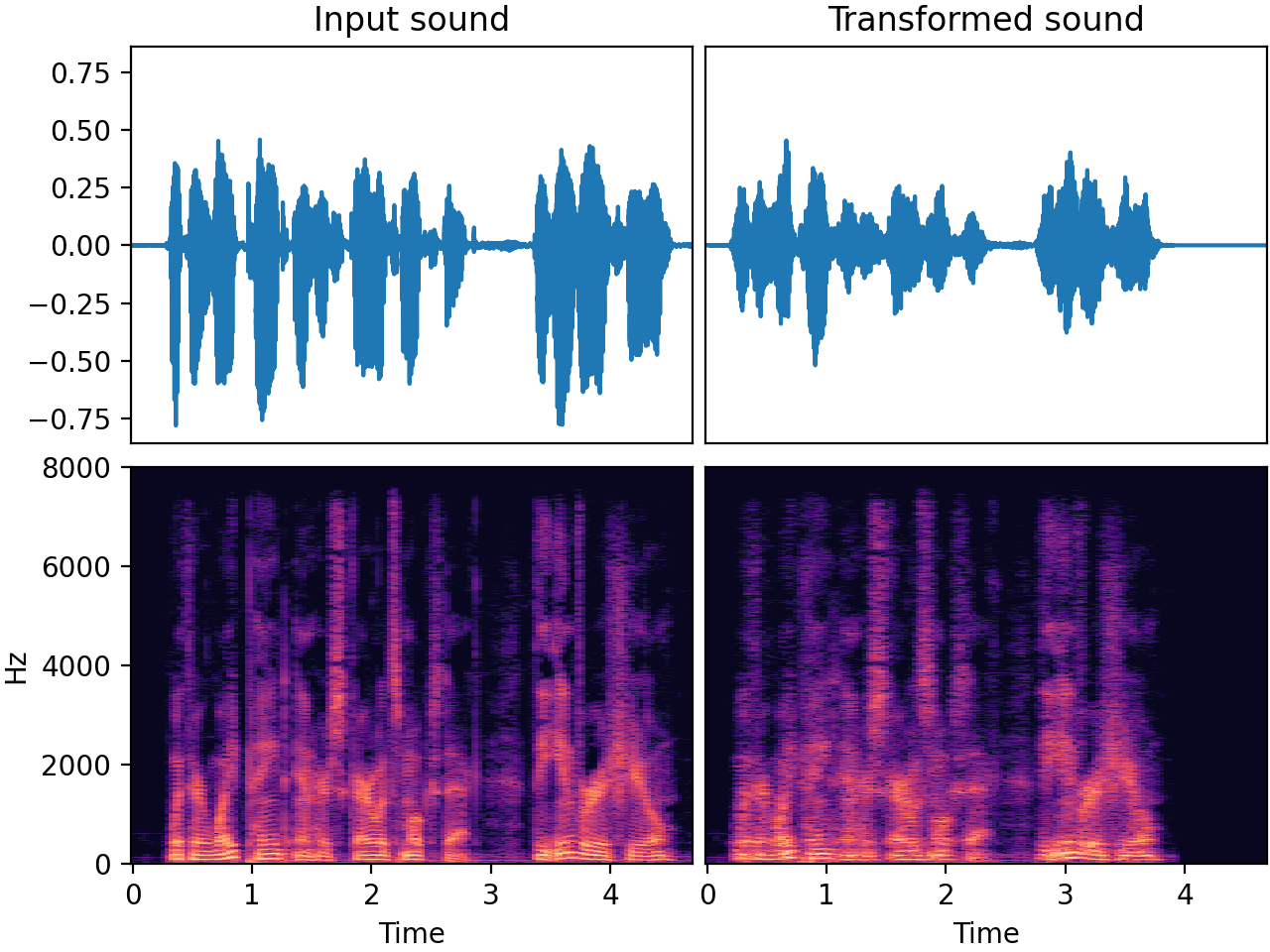
| Input sound | Transformed sound |
|---|---|
Usage example
from audiomentations import TimeStretch
transform = TimeStretch(
min_rate=0.8,
max_rate=1.25,
leave_length_unchanged=True,
p=1.0
)
augmented_sound = transform(my_waveform_ndarray, sample_rate=16000)
TimeStretch API
min_rate:float• range: [0.1, 10.0]- Default:
0.8. Minimum time-stretch rate. Values less than 1.0 slow down the audio (reduce the playback speed). max_rate:float• range: [0.1, 10.0]- Default:
1.25. Maximum time-stretch rate. Values greater than 1.0 speed up the audio (increase the playback speed). leave_length_unchanged:bool- Default:
True. IfTrue, the output audio will have the same duration as the input audio. IfFalse, the duration of the output audio will be altered by the time-stretch rate. method:str• choices:"librosa_phase_vocoder","signalsmith_stretch"-
Default:
"signalsmith_stretch"."signalsmith_stretch": Use signalsmith-stretch. It is 50-100% faster than librosa_phase_vocoder, and provides significantly higher perceived audio quality."librosa_phase_vocoder": Use librosa.effects.time_stretch. Pro: Supports any number of channels. Con: phase vocoding can significantly degrade the audio quality by "smearing" transient sounds, altering the timbre of harmonic sounds, and distorting pitch modulations. This may result in a loss of sharpness, clarity, or naturalness in the transformed audio.
p:float• range: [0.0, 1.0]- Default:
0.5. The probability of applying this transform.